Benefits of Collagen
What is Collagen?
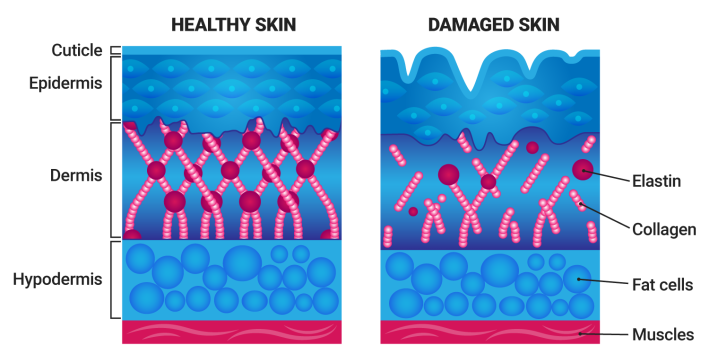
Collagen is a long-chain amino acid that gives skin its elasticity, strengthens hair, and supports connective tissue. Collagen supplements can be made from bovine or marine sources. Gelatin is removed from the sources and converted into tiny collagen peptides that are more bioavailable for humans. There are different types of collagen: Type I and Type III collagen help support skin; Type II collagen is often used to relieve joint pain.
Uses for Collagen
-
Reduce Joint Pain
Collagen plays an important role in healthy joints, as all areas of connective tissue in the body contain this protein. The results of a study involving 80 patients with progressive osteoarthritis (OA) suggests supplementing with 2,000 milligrams (mg) of collagen daily results in less pain and better joint function in those with knee or hip OA.
One study showed that supplementing with 5 grams (g) of collagen per day for 12 weeks also significantly reduced exercise-induced joint pain in young adults, ages 18 to 30.
-
Boost Skin Elasticity
Collagen is the protein that gives skin its firm, supple, and youthful appearance. Sun exposure damages skin, causes collagen to age, and leads to wrinkles. Collagen supplements can help: on one study, supplementing with collagen daily (along with hyaluronic acid) for two months improved skin appearance in terms of wrinkles, dryness, and firmness. Similar results occurred when middle-aged women took daily collagen supplements (with some women taking 2.5 g and others taking 5 g) compared to those who took a placebo for two months. By the end of the study there was a noticeable difference, with the skin of the collagen users appearing smoother, more elastic, and less saggy.
-
Improve Skin Moisture
A double-blind study of 69 women ranging in age from 35 to 55 indicates regular supplementation with collagen peptides can improve skin elasticity, and may improve skin moisture as well.
These results were seen in both a group of women who received 2.5 g of collagen hydrolysate (CH) or 5 g of CH once daily for eight weeks. Another study that had 72 women ages 35 and older take a daily mixture of 2.5 g of collagen peptides plus skin-supportive nutrients, including vitamins C and E and biotin, found that in 12 weeks, skin hydration, elasticity, roughness, and density were all significantly improved. The results remained true at a four-week follow-up.
-
Diminish Cellulite
Research indicates that cellulite, which plagues women of all ages, may be reduced by regular ingestion of bioactive collagen peptides (BCP).
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, 105 women aged 24 to 50 with moderate cellulite were given an oral dose of BCP or a placebo for six months. Normal weight women saw a statistically significant decrease in cellulite after six months, and overweight women also achieved some improvement, though not as pronounced.
“Skin waviness on thighs” decreased significantly in women of normal body weight, according to the study.
Topical Collagen vs Collagen Supplements
Both collagen and hyaluronic acid are larger molecules, which generally make skin absorption more troublesome. Dietary supplements in pill form might be a better bet with these skin boosters.