Excerpted with permission from Road to Ananda: Simple Guide to the Endocannabinoid System, Hemp Phytocannabinoids/CBD and Your Health by Carl Germano, CNS, CDN ($21.65, Healthy Living Publishing, 2018)
The presence of endocannabinoids in our bodies is abundant. Researchers find more endocannabinoid receptors than the neurotransmitter receptors of serotonin and dopamine. In total, the number of endocannabinoid receptors in the body is believed to be greater than all other neurotransmitter receptors combined.
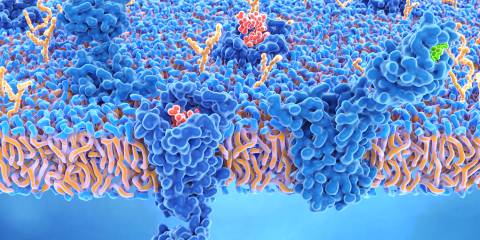
Receptors are proteins that act as doorways on the surface of cells for messengers to deliver information into the cell. They act as the cell’s eyes and ears for what is happening in the body. Every cell in every organ has specialized receptors to react to signaling throughout the body. Compounds that have the ability to sit at the doorway to deliver messages into the cell are called ligands. Ligands you may be familiar with are neurotransmitters and hormones that bind to receptors to initiate certain and specific activities.
Endocannabinoid receptors, cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2), live on the surface of cells and act as the binding sites for the endocannabinoids we produce in the body (anandamide, 2-AG). They are also influenced directly and indirectly by many plant cannabinoids (phytocannabinoids) we consume.
Hemp extracts represent a highly concentrated source of phytocannabinoids. Hemp’s most popular and dominant phytocannabinoid is called cannabidiol or CBD. However, CBD is only one of 100-plus phytocannabinoids present in hemp that are equally important or more effective than CBD in addressing certain conditions. Most notably, the phytocannabinoids CBG (cannabigerol), CBC (cannabichromene), CBN (cannabinol), and BCP (beta caryophyllene) are but a few that are equally important.
CB1 Receptors
CB1 receptors are abundant in the brain, especially in the cerebellum, basal ganglia, hippocampus, amygdala, hypothalamus, and spinal cord regions. They play significant roles in regulating pain signaling, memory processing, movement, motor control, and many other neurological functions. In addition to their concentration in the brain, CB1 receptors reside in the cardiovascular system, digestive tract, heart, liver, lungs, and immune system as well as other parts of the body. Their presence in these regions expands their activity to include functional roles in bone, heart, liver, and immune modulation.
CB2 Receptors
CB2 receptors are predominant in the brain and immune system, but are present throughout the entire body. Researchers have found an abundant amount of CB2 receptors scattered throughout the brain along with its CB1 counterpart. In addition, CB2 receptors are present in our bones, as well as peripheral organs such as the spleen, liver, and pancreas. As situated in these organ systems, CB2 receptors have many roles, including immune modulation, bone mass enhancement, brain protection, pain and inflammation control, liver support, and healthy stress response.